North Korea focuses on crypto

North Korean hackers use sophisticated Mac Mac supplied through false invitations to zoom to penetrate Web3 and crypto, theft of sensitive data in avoiding standard security measures.
Security scientists have identified a sophisticated campaign of North Korean hackers using new malware to target Web3 and cryptocurrencies on MacOS systems.
The Sentinelona Labs report describes a multi -stage attack chain. This offensive chain of social engineering, apples and binaies compiled in the programming language of them.
They are unusual for macos, which complicates detection. Operations called “Nimdoor” show the evolving tactics of groups of DPRK threats to endanger security defense and stole sensitive data from the cryptometer.
How the attack works
The initial compromise often begins with social engineering. The attackers embark on trustworthy contacts over the telegram and lure the victim for planning calls to enlarge through calendar links.
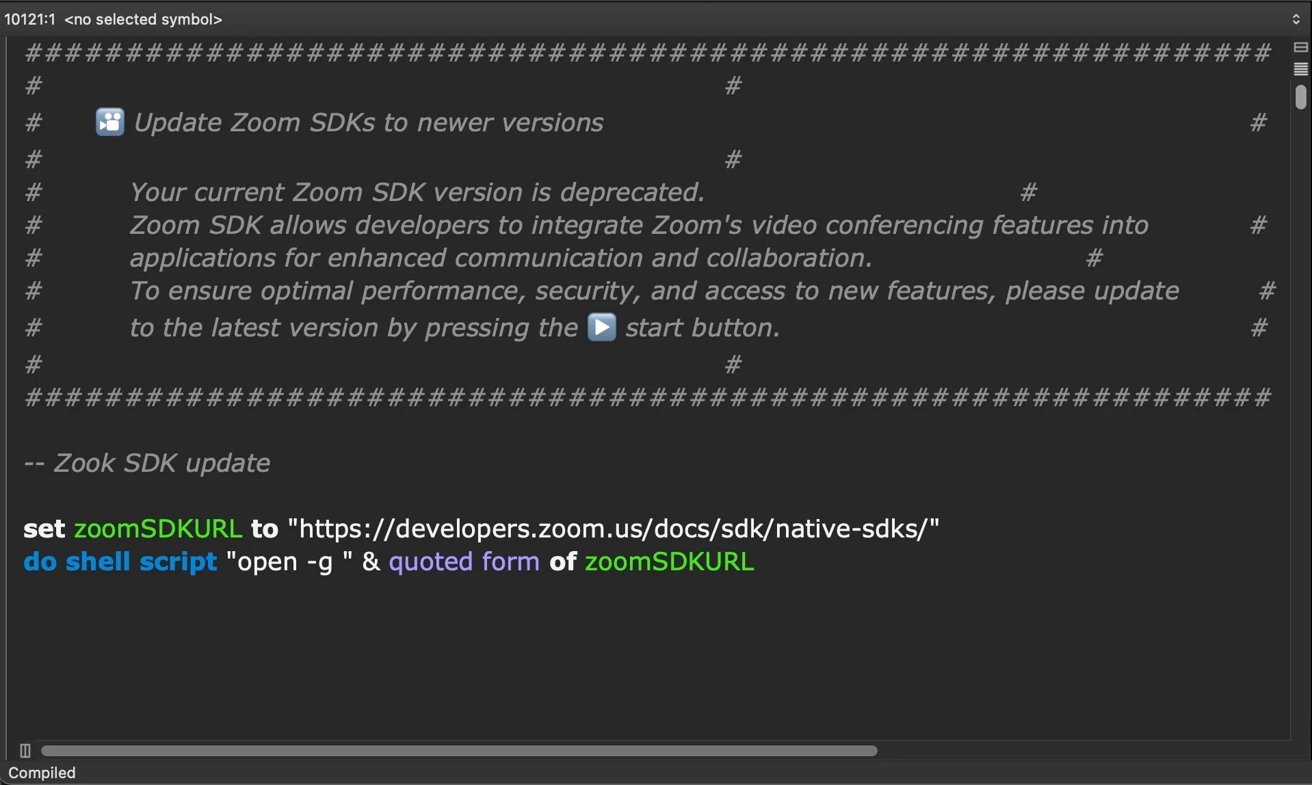
The zoom_sdk_support.scpt file contains 10,000 lines of padding with “Zook” Intead of “Zoom”. Credit picture: Sentinelona
Victims receive phishing emails with malicious SDK update scripts, which are AppleScript files with beans. These scripts have thousands of padding lines that avoid detection and load other malware from servers controlled by an attacker that mimic the legitimate domain of zoom.
After these scripts, they will download additional useful loads into the victim’s machine. Scientists have found that two primary mach-o binaies-one written in C ++ and others in them deployed in the tandem on mainain persist and steal data.
Malware uusals unusual techniques for macOS, such as a process injection with special justified. It also uses encrypted communication over websockets (WSS) and signal -based persistence mechanisms.
These mechanisms reinstall malware when the user attempts to exit or when the system restarts.
Advanced theft and persistence of data
Data exfiltration is performed via Bash Bash scripts that scrape browser history, key mechanisms and telegram data. Targeted browsers include Arc, Brave, Firefox, Chrome and Microsoft Edge.
Malware is also stealing encrypted local telegram database for potential off -up cracking.
Persistence is achieved by smart use of MacOS laundry and deceptive conventions of naming. For example, the installation of malware binary files with names such as “Google LLC”, replacing the “I” capital for Loercase “L” to connect with legitimate Google files.
Another binary “corecigent” monitors the signals system to reinstall if it is terminated. It includes measures against analysis such as 10 -minute asynchronous sleep cycles to thwart security quarantines.
The Binary Ninja view shows how to process malware processing. Credit picture: Sentinelona
According to Sentinelony, the use of them is for these binary files development in actors with threats. The implementation and interleaving of the developer and running code makes them more difficult by static analysis.
Applescript based on Beaconing provides a light command and control. It will do this without relying on heavy frameworks after exposure, which could easily trigger a warning.
How to stay safe from Nimdoor
Users should avoid starting scripts or updating software accepted through immense e -mails or messages, although they seem to come from trusted contacts. Careful URL inspection is important because attackers often create search domains to cheat the victim.
Next, keep MacOS and all installed applications updated by the latest security fixes. Updated applications reduce the vulnerability that the campaign malware use.
It also helps to use the endpoints that can detect suspicious behavior such as injections, harmful applips or unrecognizing starting agents. Regular inspection of login items and laundry can regularly detect unauthorized items that maintain the persistence of maintenance.
Finlly, accept strong, unique passwords and enable multi -factor verification if available.
(tagstranslate) Apple

